How Do AI Detectors Work? The Secrets of Spotting AI Text
Written By
Published On
Read Time

AI content is all around us. The rise of ChatGPT has led to an increase in AI-generated blogs, articles, emails, resumes, and academic papers. As a result, AI content detectors have become more common.
Schools and publications have long used AI-driven plagiarism checkers. With more people attempting to present AI-created content as their own, these tools have evolved to identify AI-generated text as well. If you haven't come across these detectors yet, you might have heard about them. But how does AI detection work? Let's find out.
What is AI detection?
AI detection refers to the methods and tools used to identify whether a piece of content was generated by artificial intelligence or by a human. With the advent of sophisticated AI models like ChatGPT, the line between human-written and AI-generated text has blurred significantly. AI detection tools are designed to analyze various features of the text to determine its origin. These tools have become increasingly important in sectors such as education, publishing, and content moderation to ensure the authenticity of written work.
Who uses AI detection tools?
AI detection tools are employed by a diverse range of professionals and organizations to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and originality of written content. These tools are crucial in various sectors, from education to publishing and beyond. Here’s a detailed look at who uses AI detection tools and why they are essential.
Educators and Academic Institutions
Educators and academic institutions are among the primary users of AI detection tools. These tools help ensure that students are submitting original work and not relying excessively on AI-generated content for their essays and assignments. With the rise of AI writing assistants like ChatGPT, there is a growing concern that students might use these tools to complete their academic tasks. AI detection tools analyze the text for signs of AI generation, such as low perplexity and burstiness, to determine the likelihood of AI involvement.
Ensuring Academic Integrity: By using AI detection tools, educators can maintain academic integrity and uphold the standards of education. These tools can identify AI-generated text, helping to prevent academic dishonesty.
Assessment Fairness: Ensuring that all students are graded based on their own work promotes fairness in assessment and evaluation processes.
Publishers and Content Writers
Publishers and content writers use AI detection tools to verify the originality of the content they produce and publish. This is crucial in maintaining the credibility and reliability of published material. Publishers need to ensure that the content they distribute is not only original but also free from AI-generated manipulation.
Quality Assurance: By detecting AI-generated content, publishers can ensure the quality and authenticity of their publications. This helps in maintaining trust with their audience.
Plagiarism Prevention: AI detection tools assist in identifying content that may have been generated by AI and subsequently manipulated to appear original, thereby preventing subtle forms of plagiarism.
Journalists and Editors
Journalists and editors use AI detection tools to verify the authenticity of articles and reports. In an era where misinformation can spread rapidly, ensuring that news articles are genuinely written by human authors is crucial.
Editorial Standards: Maintaining high editorial standards requires verifying that content is human-generated and adheres to journalistic integrity.
Misinformation Prevention: AI detection tools help identify AI-generated content that may be used to spread misinformation or fake news, thus protecting the credibility of news outlets.
Businesses and Marketers
Businesses and marketers use AI detection tools to ensure the content used in marketing campaigns and business communications is original and engaging. AI-generated content can sometimes lack the personal touch and creativity needed to connect with audiences effectively.
Brand Trust: Ensuring that marketing content is human-generated helps maintain brand trust and authenticity.
SEO Optimization: Original content is crucial for SEO. AI detection tools help businesses avoid penalties from search engines that may arise from using low-quality AI-generated content.
Recruiters and Hiring Managers
Recruiters and hiring managers use AI detection tools to verify the authenticity of job applications, including resumes and cover letters. This ensures that candidates are presenting their own qualifications and experiences.
Authenticity Verification: AI detection tools help confirm that application materials are genuinely authored by the applicants.
Fair Hiring Practices: Ensuring the authenticity of application materials promotes fair hiring practices and prevents candidates from gaining unfair advantages through the use of AI tools.
Researchers and Academics
Researchers and academics use AI detection tools to ensure the originality of their publications and to review the work of their peers. Academic integrity is crucial in research, and AI detection tools help maintain the trustworthiness of scholarly work.
Publication Integrity: Ensuring that research papers and academic articles are free from AI-generated content helps maintain the integrity of academic publications.
Peer Review Process: AI detection tools assist in the peer review process by identifying potential AI-generated content, ensuring that only original research is published.
Social Media Moderators and Platforms
Social media platforms and moderators use AI detection tools to identify and remove AI-generated content that may be used for spamming or spreading misinformation. These tools are essential in maintaining the integrity of social media platforms.
Content Moderation: AI detection tools help moderators identify and remove AI-generated spam and misinformation, ensuring that social media platforms remain trustworthy and safe for users.
Community Standards: By detecting and removing AI-generated content, social media platforms can enforce community standards and prevent the spread of harmful content.
How to detect AI writing manually?
Distinguishing between human-written and AI-generated content has become increasingly challenging. While AI detection tools provide automated solutions, there are also manual methods that can help identify AI-generated text. Understanding how AI detection works and employing these techniques can be crucial for educators, publishers, and anyone concerned with the authenticity of written content. Here’s a detailed guide on how to detect AI writing manually.
Here are several key strategies for manually detecting AI-generated writing:
Examine Sentence Structure and Length
Uniformity: AI-generated text often exhibits uniform sentence lengths and structures. Look for repetitive patterns where sentences are consistently medium in length without much variation.
Monotony: AI text can sometimes appear monotonous due to the lack of complex or varied sentence constructions.
Analyze Word Choice and Vocabulary
Repetition: AI-generated content might repeat certain words or phrases more frequently than human-written content. This is because AI models, while sophisticated, still tend to recycle the most probable word sequences.
Unusual Phrasing: AI might use odd or slightly off phrasing that doesn’t quite match natural human expression. This can be a giveaway that the text was generated by an AI.
Check for Creativity and Originality
Generic Statements: AI text often includes broad, non-specific statements lacking in-depth analysis or unique insights. Human writing typically shows more originality and specific details.
Bland Language: AI tends to avoid overly creative language and might not use idioms, colloquialisms, or cultural references as frequently as humans.
Assess Coherence and Logic
Logical Flow: AI-generated text might lack logical flow and coherence in arguments. It can sometimes present disjointed ideas that don’t logically connect.
Consistency: Look for inconsistencies in the narrative or argument. Human writers are more likely to maintain a consistent thread throughout their writing.
Politeness and Formality
Overly Polite Language: AI tools often default to overly polite and formal language. If the text appears unusually polite or formal without a clear reason, it might be AI-generated.
Hedging Language: AI-generated content often uses hedging phrases like “It’s important to note that…” or “Some might say that…” excessively to avoid making definitive statements.
Check for Semantic Depth
Shallow Content: AI writing might lack semantic depth, producing content that sounds plausible but lacks substance. If the text seems to skirt around providing deep insights or detailed explanations, it could be AI-generated.
Topic Redundancy: AI can sometimes generate redundant content, reiterating the same points in slightly different ways without adding new information.
Evaluate for Common AI Markers
Predictability: If the text feels too predictable and free of surprises, it might be AI-generated. Human writing often includes unexpected turns of phrase and unique expressions.
Redundant Phrases: AI-generated text might include redundant phrases that do not add value to the content. Look for unnecessary repetition or filler content.
How Does AI Detection Work?
AI detection works by employing advanced algorithms and natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze text and determine its origin—whether it was created by a human or generated by an artificial intelligence tool like ChatGPT. The process involves multiple methods, each focusing on different linguistic and statistical properties of the text. Here’s a comprehensive look at how AI detection functions, with an emphasis on key concepts such as perplexity, burstiness, potential alternatives like watermarks, and common mistakes that can signal AI-generated content.
Perplexity
Perplexity measures how predictable a text is. It is a key indicator used in AI detection to assess whether a piece of content is likely generated by AI.
Definition: Perplexity quantifies the uncertainty a language model has when predicting the next word in a sequence. Lower perplexity indicates higher predictability, which is typical of AI-generated text, as these models aim to produce coherent and smooth sentences.
Application in Detection:
AI-Generated Text: Tends to have low perplexity because AI models are designed to create logical, predictable sequences of words. This predictability can make the text seem fluent but somewhat monotonous and lacking in creativity.
Human-Written Text: Generally exhibits higher perplexity due to the diverse and unexpected word choices humans make, reflecting a broader range of creativity and spontaneity.
Example: Consider the sentences “I couldn’t get to sleep last night” (low perplexity) versus “I couldn’t get to sleep last time I drank coffee in the evening” (higher perplexity). The first is straightforward and predictable, while the second includes more nuanced and varied language typical of human writing.
Burstiness
Burstiness measures the variation in sentence length and structure within a text. It is another crucial factor in AI detection.
Definition: Burstiness evaluates the degree of variation between short and long sentences. High burstiness indicates a mix of different sentence lengths and structures, which is more common in human writing.
Application in Detection:
AI-Generated Text: Often displays low burstiness, as AI tends to generate sentences of similar length and structure to maintain coherence and fluency. This uniformity can make the text appear dull and less dynamic.
Human-Written Text: Features higher burstiness with a natural mix of short, punchy sentences and longer, more complex ones. This variability adds a more engaging and authentic feel to the writing.
Example: A paragraph with varied sentence lengths—"The sun set. It was a beautiful evening, full of colors and calm. Birds chirped, creating a melody that harmonized with the rustling leaves"—exhibits high burstiness compared to a uniform paragraph where all sentences are of similar length and structure.
A potential alternative: Watermarks
Watermarks are a proposed method to reliably identify AI-generated text by embedding an invisible marker within the content.
Definition: A watermark in AI-generated text would be an imperceptible code or pattern inserted by the AI model itself. This watermark could be detected by specialized tools to confirm the origin of the text.
Advantages:
Reliable Identification: Watermarks could provide a definitive method for identifying AI-generated content, reducing the ambiguity that comes with statistical measures like perplexity and burstiness.
Consistency: Unlike current detection methods that rely on linguistic analysis, watermarks would offer a more straightforward and less error-prone solution.
Challenges:
Implementation: Embedding watermarks in AI-generated text requires cooperation from AI developers and platforms, which may not always be feasible.
Detection: Developing robust tools to detect these watermarks without infringing on the usability and readability of the text poses a technical challenge.
Check for common mistakes
AI-generated content often contains specific types of errors and inconsistencies that can serve as indicators of its artificial origin.
Repetitive Phrasing and Redundancy: AI text can exhibit repetitive use of certain phrases or words due to its training on large datasets where some patterns are overrepresented. Look for unnaturally repeated terms or ideas.
Logical Inconsistencies: AI models might produce content that, while grammatically correct, lacks logical coherence. This can include contradictions, nonsensical statements, or disjointed arguments.
Overly Formal or Polite Language: AI-generated text often defaults to a very polite and formal tone, which can seem unnatural in contexts that typically require more casual language.
Lack of Deep Insights: AI tends to generate content that is broad and lacks the depth and originality of human thought. It may cover a topic superficially without providing unique insights or detailed analysis.
Example: AI text might say, “It is important to note that exercise is good for health. Furthermore, regular exercise can improve overall well-being. Exercise has many benefits.” The repetitive emphasis on "exercise" and the lack of detailed, varied points can indicate AI generation.
Techniques for identifying a text as AI-generated
Identifying AI-generated text involves sophisticated techniques that leverage advanced machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) algorithms. These techniques are designed to detect subtle patterns and anomalies that distinguish AI-generated content from human writing. Here, we explore several key methods used in AI detection, including the use of classifiers, embedding techniques, and various forms of linguistic analysis.
1. Using a classifier for AI detection
Classifiers are machine learning models trained to categorize or classify data into predefined categories, such as human-written or AI-generated. There are two main types of classifiers used in AI detection: supervised and unsupervised classifiers.
Supervised Classifiers:
Training Process: These classifiers are trained on labeled datasets where each text is pre-identified as human-written or AI-generated. The classifier learns to distinguish based on features such as vocabulary, grammar, and style.
Application: Once trained, the classifier can analyze new texts and classify them based on the patterns it has learned.
Unsupervised Classifiers:
Training Process: These classifiers work with unlabeled data, discovering patterns and structures on their own without prior categorization.
Application: Unsupervised classifiers cluster similar texts together, identifying AI-generated content based on the clusters formed.
Example: A classifier might identify AI-generated text by recognizing frequent use of specific syntactic structures or repetitive phrasing typical of AI-generated content.
2. Using embedding for detection
Embeddings represent words, phrases, or entire texts in high-dimensional vector spaces, capturing their meanings and relationships. In AI detection, embeddings are used to analyze linguistic patterns that differentiate AI-generated text from human writing.
A) Word frequency used for detection
Word frequency analysis involves examining the occurrence of specific words or phrases within a text. AI-generated content often exhibits unnatural repetition of certain terms due to its reliance on probabilistic models.
Application: By comparing the frequency of words in a text to known patterns of AI and human writing, detection tools can identify anomalies that suggest AI generation.
Example: An AI-generated text might repeatedly use phrases like "in conclusion" or "it is important to note" more often than a human writer would.
B) N-gram analysis used for detection
N-gram analysis involves examining sequences of 'n' words in a text (bigrams for two words, trigrams for three, etc.) to identify patterns.
Application: N-gram analysis can reveal repetitive or predictable sequences typical of AI-generated text, as AI models often generate content based on the most probable next word in a sequence.
Example: A text analyzed with bigrams might reveal sequences like "is important" or "to note" occurring with high frequency, indicating AI generation.
C) Syntactic analysis used for detection
How does AI detection work for essays using syntactic analysis?
Syntactic analysis examines the grammatical structure of sentences, identifying patterns in the arrangement of words and phrases.
Application: AI-generated text may adhere too strictly to grammatical rules or exhibit unusual syntactic structures that are less common in human writing.
Example: An AI-generated essay might consistently use simple, well-formed sentences without the grammatical errors or stylistic variations typical of human writing.
D) Semantic analysis for detection
How does the AI detection work using semantic analysis?
Semantic analysis focuses on the meaning and coherence of the text, examining how well ideas are developed and connected.
Application: AI-generated content might lack the depth and nuance of human writing, often producing generic or shallow content. Semantic analysis can identify these deficiencies.
Example: A semantic analysis might find that an AI-generated text discusses a topic in a repetitive or superficial manner without providing in-depth analysis or new insights.
How accurate are AI content detectors?
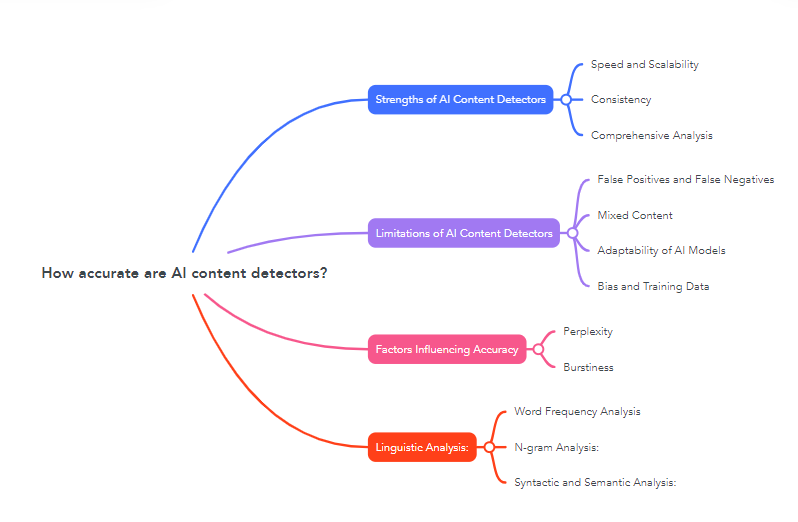
AI content detectors have become essential tools in various fields, from education to publishing, where ensuring the authenticity and originality of content is crucial. These detectors use sophisticated algorithms to analyze text and determine whether it was generated by artificial intelligence. However, the accuracy of these tools can vary significantly. Here’s a detailed look at the factors influencing the accuracy of AI content detectors, including their strengths and limitations.
Factors Influencing Accuracy
AI detection relies on several key techniques, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The primary factors influencing the accuracy of AI content detectors include:
Perplexity: Perplexity measures how predictable a piece of text is. AI-generated content often has lower perplexity due to its smooth and coherent structure, making it easier to detect. However, advanced AI models are increasingly capable of producing text with higher perplexity, similar to human writing.
Burstiness: Burstiness assesses the variation in sentence length and structure. Human writing typically exhibits higher burstiness, with a mix of short and long sentences. AI-generated text may lack this variation, making it easier to spot. However, sophisticated AI models are improving at mimicking human burstiness patterns.
Linguistic Analysis:
Word Frequency Analysis: AI-generated text might repeat certain words or phrases more frequently than human-written text. This repetitive pattern can be a clue, but it is not always a definitive indicator.
N-gram Analysis: This technique examines sequences of words (bigrams, trigrams) to identify repetitive or predictable patterns. While useful, this method can be less effective if the AI model uses varied and complex n-grams.
Syntactic and Semantic Analysis: These methods analyze grammar, sentence structure, and the overall meaning of the text. AI-generated content might have perfect grammar but lack deep semantic coherence, or it might use unusual syntactic structures.
Strengths of AI Content Detectors
AI content detectors have several strengths that contribute to their effectiveness:
Speed and Scalability: AI detectors can quickly analyze large volumes of text, making them ideal for use in educational institutions, publishing, and content moderation on social media platforms.
Consistency: These tools provide consistent results, applying the same criteria to every piece of text they analyze. This consistency can be an advantage over human evaluators, who might have varying levels of expertise and subjective biases.
Comprehensive Analysis: AI detectors can simultaneously apply multiple techniques, such as perplexity, burstiness, and various forms of linguistic analysis, to assess the likelihood that a text is AI-generated.
Limitations of AI Content Detectors
Despite their strengths, AI content detectors have notable limitations:
False Positives and False Negatives:
False Positives: These occur when human-written text is incorrectly flagged as AI-generated. This can happen when the human writer uses a style or vocabulary similar to AI-generated content.
False Negatives: These occur when AI-generated text is not detected and is mistakenly identified as human-written. Advanced AI models can produce highly convincing text that mimics human writing styles, making detection challenging.
Adaptability of AI Models: AI writing models are constantly evolving, becoming better at mimicking human writing. This rapid advancement makes it difficult for detection tools to keep up, as they need to continuously update their algorithms to recognize new patterns.
Mixed Content: AI content detectors often struggle with texts that combine human and AI-generated sections. This hybrid content can confuse the detectors, leading to inaccurate results.
Bias and Training Data: The accuracy of AI detectors depends heavily on the quality and diversity of the training data. Biases in the training data can lead to skewed detection results, where certain writing styles or topics are more likely to be misidentified.
Can AI content detectors be wrong?
AI content detectors are sophisticated tools designed to distinguish between human-written and AI-generated text. While these tools are becoming increasingly advanced, they are not infallible. Understanding the potential for errors in AI detection is crucial for users relying on these tools for academic, professional, or editorial purposes. Here’s an in-depth look at the reasons why AI content detectors can be wrong and the implications of these inaccuracies.
False Positives and False Negatives
AI detection operates by analyzing patterns, structures, and linguistic features in text. However, this process is susceptible to errors, leading to false positives and false negatives.
False Positives:
Definition: A false positive occurs when a human-written text is incorrectly flagged as AI-generated.
Causes: False positives can arise when human writing closely mimics the patterns typical of AI-generated text. For example, a highly structured essay with consistent sentence length and formal tone might be mistaken for AI content.
Implications: This can lead to unwarranted accusations of plagiarism or dishonesty, particularly in educational settings where academic integrity is paramount.
False Negatives:
Definition: A false negative occurs when AI-generated text is mistakenly identified as human-written.
Causes: Advanced AI models like GPT-4 are capable of producing text that closely resembles human writing, making detection difficult. If the AI-generated content is highly sophisticated, it might bypass detection algorithms.
Implications: False negatives can undermine the purpose of AI detection tools, allowing AI-generated content to be used deceptively in academic, professional, or editorial contexts.
Rapid Advancements in AI Models
AI detection software relies on patterns and statistical anomalies to identify AI-generated content. However, as AI models evolve, they become better at mimicking human writing, which poses significant challenges for detection tools.
Improvement in AI Capabilities: Modern AI models can generate text that is contextually relevant, semantically coherent, and stylistically nuanced, closely resembling human writing. This evolution reduces the effectiveness of traditional detection methods based on simpler models.
Lag in Detector Updates: AI detectors must continuously update their algorithms to keep pace with advancements in AI writing models. Delays in these updates can lead to reduced accuracy in detecting the latest AI-generated content.
Mixed Content and Contextual Challenges
Essays and other forms of mixed content, which combine AI-generated and human-written sections, present unique challenges for AI detection tools.
Hybrid Content: When a piece of writing includes both human and AI-generated sections, detectors may struggle to accurately assess the text. The human-written parts can mask the AI-generated sections, leading to incorrect evaluations.
Contextual Understanding: AI detectors analyze text based on linguistic and statistical features, but they lack deep contextual understanding. They may fail to recognize the broader context or logical flow of the text, leading to misclassification.
Bias and Limitations in Training Data
The effectiveness of AI text detection tools depends heavily on the quality and diversity of the training data used to develop the detection algorithms.
Training Data Bias: If the training data is biased or not representative of the wide variety of human writing styles, the detector may produce skewed results. For instance, it might be more likely to flag text from non-native English writers as AI-generated due to linguistic differences.
Generalization Issues: Detectors trained on specific datasets might struggle to generalize their findings to new or diverse types of writing. This limitation can result in inaccurate assessments when the text deviates from the patterns seen in the training data.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Several case studies and practical applications highlight the challenges and inaccuracies of AI content detectors:
Educational Institutions: Schools and universities use AI detectors to ensure academic integrity. However, there have been instances where genuine student work was incorrectly flagged as AI-generated, causing significant distress and confusion among students.
Publishing and Journalism: Publishers rely on AI detectors to maintain the authenticity of their content. In some cases, AI-generated articles have slipped through undetected, raising concerns about the reliability of these tools.
Some examples of content detectors failing
AI content detectors are designed to differentiate between human-written and AI-generated text using advanced algorithms and linguistic analysis. Despite their sophistication, these tools can and do fail in certain situations. Understanding these failures can shed light on the limitations of current AI detection technology and highlight areas for improvement. Here are some notable examples and explanations of why content detectors might fail.
Educational Context Failures
In educational settings, AI detectors are used to ensure academic integrity by identifying AI-generated essays. However, these tools can sometimes produce false positives or negatives, leading to significant consequences.
Texas A&M Incident:
Description: At Texas A&M, a professor used an AI detector to assess student essays and found that the tool flagged numerous submissions as AI-generated.
Outcome: The detector incorrectly identified human-written essays as AI-generated, causing students to be wrongly accused of academic dishonesty. This led to confusion and distress among students and highlighted the tool's limitations.
Reason for Failure: The AI detector struggled with essays that had a structured and formal style, common in academic writing, leading to false positives.
Turnitin's Misclassification:
Description: Turnitin, a widely used plagiarism detection tool, introduced an AI detection feature to identify text generated by AI models like ChatGPT. However, it faced issues with accuracy.
Outcome: In a test involving high school essays, Turnitin's tool incorrectly tagged a significant portion of human-written essays as AI-generated.
Reason for Failure: The detector's algorithms may not have been adequately trained on diverse student writing styles, leading to misclassifications.
Publishing and Journalism Failures
Publishers use AI detectors to maintain content authenticity and credibility. However, these tools can fail to accurately identify AI-generated content, leading to the publication of AI-written articles.
Journalism Mix-Ups:
Description: News organizations have inadvertently published AI-generated articles without proper attribution, relying on detection tools that failed to flag these texts.
Outcome: The credibility of these organizations was questioned when readers discovered that the published content was AI-generated.
Reason for Failure: Advanced AI models can generate text that closely mimics human writing, making it difficult for detection tools to distinguish between the two.
Literary Magazines:
Description: Literary magazines that pride themselves on human creativity and originality have faced challenges with AI detectors failing to identify AI-generated submissions.
Outcome: AI-generated stories and poems were published, undermining the magazines' commitment to showcasing human talent.
Reason for Failure: AI models can create content with deep thematic elements and stylistic nuances, posing a challenge for detectors that rely on simpler linguistic patterns.
Challenges with Mixed Content
Detecting AI-generated content in mixed texts, where both human and AI-generated sections are present, is particularly challenging.
Hybrid Texts
Description: Writers might combine AI-generated paragraphs with their own writing, creating hybrid texts that are difficult to classify.
Outcome: AI detection tools often fail to accurately assess such texts, either missing the AI-generated sections or misidentifying human-written parts.
Reason for Failure: The presence of both AI and human writing in a single document can confuse the detection algorithms, which are designed to analyze homogeneous text samples.
Limitations of Current Algorithms
AI text detection relies on various algorithms that can have inherent limitations.
Bias in Training Data:
Description: AI detectors are trained on datasets that may not fully represent the diversity of human writing styles and topics.
Outcome: This bias can lead to false positives or negatives when the detectors encounter texts that differ significantly from the training data.
Reason for Failure: Inadequate or biased training data can limit the detector's ability to generalize across different writing styles and contexts.
Rapid Evolution of AI Models:
Description: AI models like GPT-4 are continuously improving, producing text that is increasingly difficult to distinguish from human writing.
Outcome: Detection tools may become outdated quickly, struggling to keep up with the latest advancements in AI text generation.
Reason for Failure: The rapid evolution of AI models requires constant updates to detection algorithms, which can be challenging to implement in real-time.
AI detectors vs. plagiarism checkers
In the realm of ensuring content authenticity and originality, both AI detectors and plagiarism checkers play crucial roles. While they might seem similar at first glance, they serve distinct purposes and operate using different methodologies. Understanding the differences between these two tools is essential for educators, publishers, and professionals who rely on accurate content verification. Here’s a comprehensive comparison of AI detectors and plagiarism checkers, detailing how each works and their respective strengths and limitations.
Purpose and Functionality
AI Detectors: Aim to identify whether content was generated by AI tools. They focus on linguistic patterns, text predictability, and structural consistency.
Plagiarism Checkers: Aim to identify copied content by comparing the text against a database of existing works. They focus on direct matches and similarity indexes.
Detection Methodologies
AI Detectors: Use machine learning models trained to recognize the unique characteristics of AI-generated text. They analyze elements like perplexity and burstiness to make their determinations.
Plagiarism Checkers: Use database comparisons to find exact or near-exact matches with previously published content. They do not analyze the style or structure of the text but rather look for direct overlaps.
Application Scenarios
AI Detectors: Useful in academic settings to ensure students are not submitting AI-generated work, in publishing to verify the authenticity of articles, and in professional contexts to ensure original content creation.
Plagiarism Checkers: Widely used in educational institutions to detect copied assignments, in publishing to prevent content theft, and in legal contexts to verify the originality of documents and reports.
Accuracy and Limitations
AI Detectors: Can struggle with advanced AI models that closely mimic human writing. They might produce false positives or negatives, particularly with hybrid content that combines AI-generated and human-written sections.
Plagiarism Checkers: Generally accurate in detecting copied text but can miss paraphrased content that maintains the original meaning. They may also produce false positives if common phrases or properly cited quotes are flagged as plagiarism.
How does AI detection work alongside plagiarism checkers in practical applications?
Both tools are integral to maintaining content integrity but must be used in complementary ways to ensure thorough verification.
Educational Institutions:
AI Detectors: Help educators ensure that essays and assignments are original and not generated by AI.
Plagiarism Checkers: Ensure that students have not copied their work from existing sources without proper attribution.
Publishing and Journalism:
AI Detectors: Ensure that published content is genuinely authored by human writers, maintaining credibility.
Plagiarism Checkers: Prevent content theft and ensure that articles are original.
Professional and Legal Contexts:
AI Detectors: Verify the authenticity of professional reports and communications, ensuring they are human-generated.
Plagiarism Checkers: Verify the originality of legal documents and reports, preventing intellectual property theft.
Which AI content detector is best?
With the rise of AI-generated content, the need for effective AI content detectors has become paramount. These tools help ensure the authenticity and originality of written work across various domains, from academic essays to professional articles. Choosing the best AI content detector depends on several factors, including accuracy, ease of use, and the specific needs of the user. Here’s an in-depth look at some of the leading AI content detectors, how they work, and which might be best suited for different applications.
Several AI content detectors stand out in the market due to their advanced capabilities and accuracy. Here’s a detailed look at some of the most prominent tools:
GPTZero:
Overview: GPTZero is designed specifically to detect content generated by OpenAI’s GPT models. It uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze text and identify AI characteristics.
Strengths: Highly effective at detecting text generated by GPT models due to its specialized focus.
Limitations: May be less effective with AI models from other developers.
Copyleaks:
Overview: Copyleaks offers a robust AI detection tool that combines plagiarism detection with AI content detection. It uses machine learning algorithms to identify both copied and AI-generated text.
Strengths: Dual functionality makes it ideal for educational institutions and publishers looking to ensure both originality and authenticity.
Limitations: The dual focus might lead to a higher rate of false positives in AI detection.
Writer.com:
Overview: Writer.com’s AI detection tool is part of a comprehensive suite designed to enhance writing quality and originality. It uses a combination of linguistic analysis and machine learning.
Strengths: Integrated with other writing enhancement tools, making it a good choice for professional writers and content creators.
Limitations: May require a subscription to access full features.
Scribbr:
Overview: Scribbr’s AI detector is geared towards academic use, helping educators ensure that student essays are original. It focuses on detecting AI-generated text in academic submissions.
Strengths: Tailored for academic use with features that address common issues in student writing.
Limitations: Primarily designed for educational settings, which might limit its applicability in other contexts.
Crossplag:
Overview: Crossplag combines AI detection with traditional plagiarism checking. It offers detailed reports and integrates with various educational platforms.
Strengths: Comprehensive reports and educational integration make it a strong choice for schools and universities.
Limitations: Its detailed approach might be overkill for simpler needs.
Comparative Analysis
Each AI detector has strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different contexts. Here’s a comparative analysis to help determine which AI content detector might be best for your needs:
Accuracy:
GPTZero and Copyleaks: Known for high accuracy in detecting AI-generated content, particularly from GPT models.
Writer.com and Scribbr: Offer good accuracy with additional features to enhance overall writing quality and academic integrity.
Ease of Use:
Writer.com: User-friendly interface and integration with other writing tools make it easy to use.
Scribbr: Designed for educators, providing a straightforward user experience tailored to academic settings.
Special Features:
Copyleaks: Combines AI detection with plagiarism checking, offering a dual functionality that is useful in educational and publishing contexts.
Crossplag: Detailed reporting and integration with educational platforms make it a comprehensive tool for academic institutions.
Cost and Accessibility:
GPTZero: May be free or have a lower cost due to its specialized focus.
Writer.com and Copyleaks: Typically require subscriptions, which might be a consideration for budget-conscious users.
Why is AI content detection so difficult to get right?
AI content detection has become a critical task across various sectors, from academia to publishing, due to the increasing sophistication of AI-generated text. Despite advancements in detection technology, accurately identifying AI-generated content remains challenging. Several factors contribute to the difficulty of getting AI content detection right. Here’s a detailed exploration of why this task is so complex, using insights from various sources.
Rapid Advancements in AI Models
One of the primary challenges in AI content detection is the rapid advancement of AI models. These models, such as GPT-4, are continually improving, making their outputs more indistinguishable from human writing.
Sophistication of AI Models: Modern AI models can produce text that mimics human writing with high accuracy, including nuanced language use, varied sentence structures, and contextually relevant content.
Adaptability: AI models learn from vast amounts of data and adapt quickly to new writing styles and formats, making it challenging for detection tools to keep pace.
Mixed Content and Contextual Understanding
Another significant challenge is detecting AI-generated content within mixed texts, where both human and AI-written sections are present.
Hybrid Texts: When human writers integrate AI-generated paragraphs into their work, it becomes difficult for detectors to accurately assess the text. The human-written sections can mask the AI-generated parts.
Contextual Understanding: AI detectors often lack deep contextual understanding. They focus on linguistic features and patterns, but might miss the broader context or logical flow that a human reviewer would catch.
Bias and Limitations in Training Data
The effectiveness of AI detectors heavily depends on the quality and diversity of their training data. Biases in this data can lead to inaccuracies.
Training Data Bias: If the training data does not represent the full spectrum of human writing styles and topics, the detector might produce skewed results. For example, it may be more likely to flag text from non-native English speakers as AI-generated.
Generalization Issues: Detectors trained on specific datasets might struggle to generalize their findings across different types of writing, leading to false positives or negatives when encountering unfamiliar styles or formats.
False Positives and False Negatives
AI content detectors can produce false positives (incorrectly flagging human-written text as AI-generated) and false negatives (failing to detect AI-generated text).
False Positives:
Cause: Occur when human-written text mimics the structured and formal style typical of AI-generated content.
Impact: This can lead to unwarranted accusations of academic dishonesty or questions about the authenticity of professional content.
False Negatives:
Cause: Occur when advanced AI-generated text closely resembles human writing, escaping detection.
Impact: This undermines the purpose of AI detection tools, allowing AI-generated content to be used deceptively in various contexts.
Rapid Evolution of Detection Tools
The rapid evolution of AI models necessitates continuous updates to detection algorithms, a task that is both technically challenging and resource-intensive.
Algorithm Updates: Detection tools must be regularly updated to recognize the latest patterns in AI-generated text. This requires significant computational resources and expertise.
Resource Intensive: Maintaining and updating AI detection algorithms is costly and requires ongoing research and development efforts.
How can AI detector tools be improved?
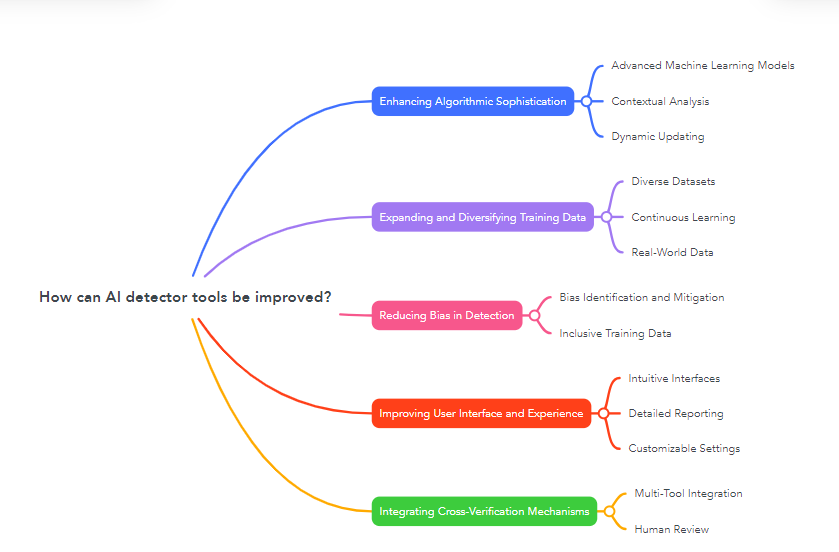
AI content detectors are crucial in maintaining the authenticity and originality of written work across various domains. However, as AI models continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the accuracy and effectiveness of these detection tools need to keep pace. Improving AI detector tools involves several strategies, from enhancing their technical capabilities to addressing inherent biases and expanding their training datasets. Here’s a detailed look at how AI detector tools can be improved.
Enhancing Algorithmic Sophistication
Improving the algorithms used in AI detection is essential for increasing accuracy and reliability.
Advanced Machine Learning Models: Utilizing more sophisticated machine learning models can enhance the ability of AI detectors to recognize subtle patterns typical of AI-generated content. This includes deep learning techniques that can analyze complex linguistic features more effectively.
Contextual Analysis: Incorporating advanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques that can understand context better will help in distinguishing between human and AI writing. This includes understanding the thematic flow and logical coherence of text.
Dynamic Updating: Implementing dynamic updating mechanisms where the detection algorithms continuously learn from new data can help keep the detectors up-to-date with the latest advancements in AI-generated text.
Example: By integrating transformer-based models like BERT or GPT into detection algorithms, AI detectors can improve their understanding of nuanced language and context, thereby reducing false positives and negatives.
Expanding and Diversifying Training Data
The quality and diversity of training data are crucial for the effectiveness of AI detectors.
Diverse Datasets: Expanding the training datasets to include a wide range of writing styles, genres, and topics will help detectors generalize better across different types of text. This can reduce bias and improve accuracy.
Continuous Learning: Incorporating mechanisms for continuous learning from new examples of AI-generated and human-written content will ensure that the detectors remain effective as AI models evolve.
Real-World Data: Using real-world data from various domains (academic, professional, creative) will help in training detectors to recognize diverse writing patterns and contexts.
Example: Training AI detectors on a dataset that includes academic essays, professional reports, creative writing, and casual blog posts can help them better recognize the varied nuances in human writing compared to AI-generated content.
Reducing Bias in Detection
Bias in training data can lead to skewed detection results. Reducing this bias is crucial for improving detector accuracy.
Bias Identification and Mitigation: Developing methods to identify and mitigate biases in the training data will help create more balanced detectors. This includes addressing biases related to non-native English speakers, different writing styles, and cultural contexts.
Inclusive Training Data: Ensuring that the training data includes diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds can help in creating detectors that are fair and accurate for all users.
Example: By analyzing the performance of AI detectors across different demographic groups and adjusting the training data accordingly, biases can be identified and reduced, leading to more equitable detection outcomes.
Improving User Interface and Experience
Making AI detection tools more user-friendly and accessible can improve their adoption and effectiveness.
Intuitive Interfaces: Developing intuitive and easy-to-use interfaces for AI detection tools will help users quickly understand and utilize the software. This includes clear instructions, user-friendly dashboards, and accessible reports.
Detailed Reporting: Providing detailed and actionable reports that explain why a text was flagged can help users understand the results and take appropriate actions. This includes highlighting specific phrases or sections that led to the detection.
Customizable Settings: Allowing users to customize detection settings based on their specific needs (e.g., educational, professional, creative) can improve the relevance and usefulness of the detection results.
Example: An AI detection tool with a user-friendly interface that offers detailed reports and customization options can help educators, publishers, and professionals effectively identify and address AI-generated content.
Integrating Cross-Verification Mechanisms
Integrating AI detection tools with other verification mechanisms can enhance their reliability.
Multi-Tool Integration: Combining AI detectors with plagiarism checkers and other verification tools can provide a comprehensive assessment of content authenticity. This integrated approach can cross-verify the results, reducing the chances of false positives and negatives.
Human Review: Incorporating human review as a secondary verification step for flagged content can help ensure accuracy. This human-AI collaboration can address nuances that automated tools might miss.
Example: A workflow that integrates AI detection with plagiarism checking and includes a human review step can provide a robust mechanism for verifying the authenticity of written content.
How to bypass AI content detection?
As AI content detection tools become more sophisticated, so do the methods employed to bypass them. Understanding both how AI detection works and the strategies used to evade detection is crucial for educators, publishers, and professionals who rely on these tools. Here’s a comprehensive look at how AI content detection can be bypassed, the techniques used, and the implications of these practices.
Despite the sophistication of AI detection tools, there are several strategies that individuals can use to bypass these systems. Understanding these methods can help in refining detection technologies and developing more robust solutions.
1. Paraphrasing and Rewriting
Paraphrasing involves rephrasing the AI-generated content to make it appear more human-like.
Using Synonyms: Replacing key words with synonyms can alter the text enough to avoid detection while retaining the original meaning.
Changing Sentence Structure: Altering the structure of sentences, such as converting passive voice to active voice or vice versa, can help bypass detection.
Human Editing: Manual edits by humans can introduce natural errors, idiomatic expressions, and stylistic variations that are less likely to be flagged by AI detectors.
Example: An AI-generated sentence like "The results indicate a significant improvement in efficiency" can be paraphrased to "The findings show a notable increase in efficiency," thereby reducing its predictability and altering its structure.
2. Using AI Paraphrasing Tools
AI paraphrasing tools can automatically rewrite AI-generated content to make it less detectable.
Automated Rewriting: These tools can rephrase entire paragraphs, altering vocabulary and syntax to produce a text that appears more human-like.
Content Spinning: Content spinning tools generate multiple versions of the same text, each with slight variations to evade detection.
Example: Using an AI paraphrasing tool to rewrite a paragraph multiple times can produce versions that differ enough from the original to avoid detection, even though the core content remains the same.
3. Injecting Human-Like Errors
Introducing deliberate errors and idiosyncrasies can make AI-generated content seem more human.
Typographical Errors: Adding common typos can make the text appear less polished and more human.
Grammatical Mistakes: Introducing minor grammatical errors can mimic the natural mistakes made by human writers.
Colloquial Language: Using slang, idiomatic expressions, and conversational tones can make the text seem more authentic.
Example: An AI-generated text might be too polished, so adding typos like "teh" instead of "the" or using colloquial phrases like "a lotta" instead of "a lot of" can make it appear more human.
4. Mixing AI and Human Writing
Combining AI-generated text with human-written sections can create hybrid content that is harder to detect.
Human Introduction and Conclusion: Writing the introduction and conclusion manually, while using AI to generate the main body, can reduce the chances of detection.
Interleaving Sentences: Mixing AI-generated sentences with human-written ones within paragraphs can confuse detection algorithms.
Example: In an essay, manually writing the opening and closing paragraphs while using AI to generate the body text can help evade detection, as the most scrutinized sections appear more human.
5. Content Reformatting and Simplification
Changing the format and simplifying the content can alter the text enough to bypass detection.
Reformatting: Changing bullet points to numbered lists, altering headings, and modifying text layout can help evade detection.
Simplification: Breaking down complex sentences into simpler ones and changing complex vocabulary to more common words can reduce the likelihood of detection.
Example: Reformatting a document by changing a bullet list to a series of paragraphs or simplifying the language used in a technical report can make AI-generated content less recognizable to detection tools.
Implications of Bypassing AI Detection
While the above methods can be effective in evading AI content detectors, they have significant ethical and practical implications.
Academic Integrity: Bypassing AI detection in educational settings undermines academic integrity and can lead to unfair advantages.
Professional Credibility: In professional and publishing contexts, using AI-generated content without proper attribution can damage credibility and trust.
Technological Arms Race: As detection tools improve, so do the methods to bypass them, leading to a continuous cycle of advancement and evasion.
Who is interested in detecting whether an AI or a person makes a text?
The growing sophistication of AI-generated content has sparked significant interest in AI detection tools across various sectors. Understanding who is interested in detecting AI-generated text and why they rely on these tools is crucial for appreciating the broad impact of AI on content authenticity and integrity. Here’s a detailed look at the key stakeholders interested in AI detection and the reasons behind their interest.
Educational Institutions
Educational institutions are among the primary users of AI detection tools. They use these tools to ensure the originality and integrity of student submissions.
Ensuring Academic Integrity: Schools, colleges, and universities use AI detection software to verify that students submit original work and not essays generated by AI tools. This is crucial for maintaining academic standards and fairness.
Preventing Academic Dishonesty: By detecting AI-generated content, educators can prevent students from using AI to gain an unfair advantage, thereby upholding the value of academic credentials.
Example: A professor might use AI text detection tools to screen student essays for signs of AI involvement, ensuring that all submissions are the students' own work.
Publishers and Content Creators
Publishers and content creators need to maintain the authenticity and originality of their work to preserve credibility and trust with their audiences.
Maintaining Content Authenticity: Publishers use AI detection tools to ensure that articles, blog posts, and other content are genuinely written by humans and not generated by AI. This is essential for maintaining editorial standards.
Protecting Intellectual Property: By verifying that submitted content is human-written, publishers can protect their intellectual property and avoid legal issues related to unauthorized AI-generated content.
Example: A publishing house might implement AI detection software to screen manuscripts for AI-generated sections, ensuring the originality of the content before publication.
Businesses and Marketers
Businesses and marketers are increasingly using AI detection tools to ensure the quality and originality of their communications and marketing materials.
Ensuring Brand Integrity: Companies use AI detection tools to verify that their marketing content, such as advertisements and social media posts, is original and aligns with their brand voice.
Avoiding SEO Penalties: Search engines may penalize websites that rely heavily on AI-generated content. Businesses use AI detection tools to avoid such penalties and ensure their content ranks well in search engine results.
Example: A marketing team might use AI text detection to review content before it is published online, ensuring that it is original and engaging for their audience.
Journalists and Media Organizations
Journalists and media organizations rely on AI detection tools to maintain the credibility and reliability of news articles and reports.
Preserving Journalistic Integrity: News organizations use AI detection to ensure that their content is human-authored, preserving the integrity and trustworthiness of their reporting.
Combating Fake News: AI detection tools help media organizations identify and filter out AI-generated content that could be used to spread misinformation or fake news.
Example: A newsroom might implement AI writing detection to screen submissions from freelance journalists, ensuring that all published content meets their editorial standards.
Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms are interested in detecting AI-generated content to maintain the quality of user interactions and prevent the spread of misinformation.
Filtering Spam and Bots: Social media platforms use AI detection tools to identify and remove AI-generated posts and comments from bots, ensuring a more authentic user experience.
Preventing Misinformation: By detecting AI-generated content, social media platforms can reduce the spread of misinformation and maintain the integrity of the information shared on their platforms.
Example: A social media platform might use AI detection software to monitor and filter out AI-generated comments and posts, protecting users from spam and misleading content.
Recruiters and Hiring Managers
Recruiters and hiring managers use AI detection tools to verify the authenticity of application materials, such as resumes and cover letters.
Ensuring Candidate Authenticity: By using AI detection, recruiters can verify that application materials are genuinely authored by the candidates, ensuring the authenticity of their qualifications and experience.
Maintaining Fair Hiring Practices: AI detection tools help maintain fair hiring practices by ensuring that all candidates are evaluated based on their own merits, not AI-generated content.
Example: A hiring manager might use AI text detection to screen resumes and cover letters, ensuring that all application materials are original and reflect the candidates' true abilities.
Is Google detecting ChatGPT?
With the rapid development and widespread use of AI models like ChatGPT, questions arise about how major platforms like Google are responding to AI-generated content. Specifically, there is significant interest in whether Google can detect content produced by ChatGPT and similar AI tools, and how this might impact content indexing, ranking, and overall search engine optimization (SEO). Here’s a detailed look at this topic, exploring how AI detection works in the context of Google’s algorithms and its implications for content creators.
Google's Approach to AI-Generated Content
Google’s primary goal is to deliver the highest quality and most relevant content to its users. As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, Google has had to adapt its algorithms to ensure that the content it indexes and ranks meets its quality standards.
Content Quality Guidelines: Google emphasizes the importance of original, high-quality content. Its guidelines suggest that content should provide value, demonstrate expertise, and be written with a clear purpose.
AI Content Policies: While Google has not explicitly banned AI-generated content, it has indicated that automatically generated content intended to manipulate search rankings violates its webmaster guidelines. This includes content that is generated without adding significant value or that fails to provide a good user experience.
Example: Google’s algorithms are designed to detect low-quality, spammy content, which can include poorly executed AI-generated text. Such content may be devalued or removed from search results if it does not meet Google’s quality standards.
Technical Methods for Detecting AI Content
Google likely employs a combination of advanced machine learning techniques and human review to detect and manage AI-generated content.
Machine Learning Models: Google uses sophisticated machine learning models that can analyze text at a deep level, identifying patterns typical of AI-generated content. These models likely incorporate elements of perplexity and burstiness analysis, similar to other AI detection tools.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP techniques help Google understand the context and semantics of content, allowing it to detect whether the text aligns with natural human writing or exhibits characteristics of AI generation.
Cross-Referencing: By cross-referencing content with known databases of AI-generated text and other sources, Google can identify and flag potentially AI-generated content.
Example: Google’s machine learning models can analyze the predictability and uniformity of text to determine if it was likely generated by an AI, such as ChatGPT. If the content is flagged, it may be subject to further scrutiny or penalization.
Implications for Content Creators
For content creators, understanding Google’s stance on AI-generated content is crucial for maintaining good SEO practices and ensuring that their content performs well in search rankings.
Content Quality: To avoid potential penalties, content creators should focus on producing high-quality, original content that provides genuine value to users. Even if AI tools are used, human oversight and editing are essential to ensure the content meets Google’s standards.
Transparency: Being transparent about the use of AI in content creation can also help build trust with both users and search engines. Acknowledging AI assistance while ensuring the content is reviewed and enhanced by humans can mitigate potential issues.
SEO Best Practices: Adhering to established SEO best practices, such as using relevant keywords naturally, providing accurate information, and creating engaging, user-friendly content, remains crucial.
Example: A content creator using ChatGPT to draft articles should ensure that the final content is thoroughly reviewed and edited to add depth, correct any inaccuracies, and enhance readability. This human touch can help the content align with Google’s quality guidelines and perform better in search rankings.
The Future of AI Detection and Google
As AI models continue to evolve, so too will Google’s methods for detecting and managing AI-generated content. Staying informed about these changes and adapting strategies accordingly will be key for content creators.
Continuous Improvement: Google is likely to continue improving its AI detection capabilities, leveraging advancements in machine learning and NLP to better identify and manage AI-generated content.
Adaptive Strategies: Content creators should remain adaptable, regularly updating their knowledge of Google’s guidelines and algorithm changes to ensure their content remains compliant and competitive.
Example: Monitoring updates to Google’s webmaster guidelines and algorithm changes can help content creators stay ahead of potential penalties and ensure their content continues to rank well, even as AI detection methods become more sophisticated.
AI image and video detectors
As artificial intelligence technology continues to advance, the creation and dissemination of AI-generated images and videos have become increasingly common. This development poses significant challenges for ensuring the authenticity and integrity of visual content. AI image and video detectors play a crucial role in identifying AI-generated media, helping to prevent misinformation and maintain trust in digital content. This comprehensive exploration delves into how AI image and video detectors work, their applications, and the ongoing challenges they face.
How Does AI Detection Work for Images and Videos?
AI detection for visual content involves sophisticated techniques that analyze various aspects of images and videos to identify characteristics indicative of AI generation.
Perceptual Hashing: This technique generates a unique hash value based on the visual content. AI detectors compare these hash values against known databases of AI-generated images and videos to identify matches.
Texture and Pattern Analysis: AI detectors analyze the texture and patterns within images and videos. AI-generated content often has anomalies or inconsistencies in texture that can be identified by these tools.
Deep Learning Models: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and other deep learning models are employed to analyze pixel-level details and detect subtle artifacts left by AI generation processes.
Example: An AI detector might identify an image as AI-generated by analyzing its texture and finding inconsistencies in pixel arrangements that are characteristic of generative adversarial networks (GANs).
Applications of AI Image and Video Detectors
AI image and video detectors are applied across various sectors to ensure the authenticity of visual content.
Misinformation Prevention: Social media platforms and news organizations use AI detectors to identify and remove deepfakes and other AI-generated content that could be used to spread misinformation.
Content Moderation: Platforms like YouTube and Instagram employ AI detection tools to moderate content, ensuring that images and videos comply with their guidelines and are not misleading or harmful.
Digital Forensics: Law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity firms use AI image and video detectors in digital forensics to verify the authenticity of visual evidence and detect tampering.
Example: A news organization might use AI video detection tools to verify the authenticity of a viral video before publishing it, ensuring that it is not a deepfake intended to mislead the public.
Technical Challenges in Detecting AI-Generated Images and Videos
While text detection focuses on linguistic patterns, image and video detection must address unique technical challenges related to visual data.
High Variability: AI-generated images and videos can vary widely in quality and complexity, making it difficult for detectors to consistently identify them.
Advanced AI Techniques: Sophisticated AI models, such as GANs, can produce highly realistic images and videos, posing a significant challenge for detection tools.
Continuous Evolution: AI generation techniques are constantly evolving, requiring detection tools to be continuously updated to keep pace with new methods.
Example: Deepfake videos created using advanced GANs can be particularly challenging to detect because they can closely mimic the appearance and movements of real people, requiring detectors to use highly sophisticated analysis techniques.
Improving AI Image and Video Detectors
To enhance the effectiveness of AI image and video detectors, several strategies can be implemented:
Enhanced Training Data: Expanding the datasets used to train AI detectors to include a wide variety of AI-generated images and videos can improve their accuracy and robustness.
Advanced Algorithms: Developing more advanced detection algorithms that can analyze deeper layers of visual data and identify subtle anomalies can enhance detection capabilities.
Cross-Verification Techniques: Integrating AI detection with other verification methods, such as metadata analysis and human review, can provide a more comprehensive approach to detecting AI-generated content.
Example: By training AI detectors on a diverse dataset that includes various styles and techniques of AI-generated images and videos, and using advanced deep learning algorithms, the tools can become more adept at identifying even the most sophisticated AI creations.
What is the future of AI detection tools?
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, the capabilities of AI-generated content are becoming more sophisticated and harder to distinguish from human-created work. This evolution poses significant challenges for AI detection tools, necessitating continuous improvement and innovation. The future of AI detection tools involves enhanced technologies, adaptive strategies, and broader applications to maintain content authenticity and integrity. Here’s a detailed exploration of what the future holds for AI detection tools.
Enhanced Machine Learning Models
The future of AI detection tools will heavily rely on advancements in machine learning models and algorithms.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks: More sophisticated deep learning models, such as transformer-based architectures, will be employed to detect AI-generated content with greater accuracy. These models can analyze deeper layers of linguistic and visual data.
Adaptive Algorithms: AI detection tools will incorporate adaptive algorithms that learn and evolve as AI generation techniques become more advanced. This will enable the tools to keep pace with new AI models and generation methods.
Example: Using transformer-based models like BERT and GPT for detection can enhance the ability to understand context and nuances, leading to better identification of AI-generated content.
Expanded and Diverse Training Data
The quality and diversity of training data are crucial for the effectiveness of AI detection tools.
Comprehensive Datasets: Future AI detectors will use more comprehensive datasets that include a wide range of AI-generated and human-created content across various genres and styles. This diversity will help improve the robustness of detection algorithms.
Continuous Data Updates: Regularly updating training datasets with new examples of AI-generated content will ensure that detection tools remain effective against the latest generation techniques.
Example: Incorporating diverse datasets that include different writing styles, languages, and types of visual content can help AI detectors better generalize across various contexts and reduce bias.
Integration with Other Technologies
The future of AI detection tools will see greater integration with other technologies to enhance their capabilities.
Blockchain and Cryptographic Techniques: Using blockchain technology to create immutable records of content creation can help verify the authenticity and origin of content. Cryptographic techniques can add another layer of security and verification.
Cross-Verification Systems: Integrating AI detection tools with other verification systems, such as plagiarism checkers and human review, can provide a more comprehensive approach to content authentication.
Example: Combining AI detection with blockchain technology could provide a verifiable trail of content creation and modification, ensuring that the content's authenticity is maintained.
Addressing Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The future development of AI detection tools will need to address ethical and privacy concerns.
Ethical AI Use: Ensuring that AI detection tools are used ethically, respecting user privacy and avoiding unintended biases, will be a key focus. This involves transparent development practices and ethical guidelines.
Privacy Protection: Implementing robust data protection measures to safeguard user information while using AI detection tools will be essential.
Example: Developing AI detection tools with built-in privacy protections, such as anonymizing data and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, can help maintain user trust.
Real-Time Detection and User Accessibility
Enhancing real-time detection capabilities and user accessibility will be important for the future of AI detection tools.
Real-Time Analysis: Future AI detectors will offer real-time analysis capabilities, providing immediate feedback on the authenticity of content as it is created or shared.
User-Friendly Interfaces: Developing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces will make AI detection tools more accessible to a broader audience, including educators, content creators, and general users.
Example: Implementing real-time detection features in word processors and social media platforms can help users identify and correct AI-generated content instantly.
Conclusion
The future of AI detection tools is marked by the need for continuous innovation and improvement to keep up with the evolving sophistication of AI-generated content. These tools will rely heavily on advancements in machine learning models, expanded and diverse training datasets, and the integration of additional verification technologies.
Addressing ethical and privacy concerns will also be crucial to ensure the responsible use of AI detection. Enhancing real-time detection capabilities and improving user accessibility will make these tools more effective and widely used across various sectors, from education and publishing to business and social media. Understanding how AI detection works and continuously adapting to new AI generation techniques will be essential for maintaining content authenticity and integrity in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the ethical implications of using AI detection tools in education?
AI detection tools can raise concerns about privacy and fairness. Ensuring transparency in their use and providing clear guidelines can help address these ethical implications.
Can AI detection tools differentiate between AI-assisted and fully AI-generated content?
AI detection tools may struggle to distinguish between AI-assisted and fully AI-generated content, especially when mixed with human input. Continuous advancements aim to improve this capability.
How frequently should AI detection algorithms be updated to remain effective?
AI detection algorithms should be updated regularly, ideally in real-time, to keep pace with the rapid advancements in AI generation techniques.