Build vs. Buy Decision in Generative AI for Enterprises
Written By
Published On
Read Time

In the past one year, the world of Generative AI has seen groundbreaking developments that were once considered the stuff of science fiction. Major players like Open AI, Microsoft, and Amazon are rolling out APIs, unleashing some of the most advanced AI technologies for developers to explore. This rapid evolution is shaking up the market, prompting companies to rethink their strategies and policies for engaging with this revolutionary tech.
A key area experiencing significant change, and one we're intimately familiar with, is enterprise knowledge management. The challenge now is figuring out how companies can integrate something as powerful as ChatGPT with their own or licensed internal knowledge databases.
This leads us to a crucial decision point for many of our clients and prospects: the build vs. buy dilemma. Should businesses invest in off-the-shelf solutions, or should they harness these new APIs to craft their own custom solutions?
Pros and Cons of Building Generative AI
Building Generative AI: Pros
Customization and Control: Building your own generative AI allows for complete customization. You can tailor the AI to meet your specific needs, which is particularly beneficial if your requirements are unique.
Competitive Advantage: Developing in-house generative AI can provide a competitive edge. For example, Bloomberg created BloombergGPT, a 50-billion-parameter system, to maintain its leadership in data analysis.
Focused Application: By building your own AI, you can concentrate on core business needs. This is especially important in industries like manufacturing or pharmaceuticals, where AI can significantly enhance specific processes.
Building Generative AI: Cons
High Costs: Building generative AI from scratch is expensive. It requires significant investment in talent, infrastructure, and resources.
Resource Intensive: It demands a team of experts in machine learning, natural language processing, and more. This can be a challenge, especially since AI skills are scarce.
Ongoing Maintenance: Building your own AI isn't a one-time task. It requires continuous updates, bug fixes, and the development of new features.
From Taking to Making: The Case for Building
When it comes to the "Build vs. Buy Generative AI" debate, the decision to build generative AI in-house is a journey from merely taking existing solutions to actively making your own. This path offers several compelling advantages tailored to organizations seeking a deep integration of AI with their unique business processes and goals.
Tailored Solutions for Specific Needs
Building your own generative AI system allows for customization that aligns precisely with your organization's specific requirements. Unlike off-the-shelf products, an in-house AI can be fine-tuned to address unique challenges and opportunities within your industry or company. This level of customization ensures that the AI solution is not just a generic tool but a strategic asset that provides a competitive edge.
Leveraging In-House Expertise
Organizations with a strong base in technology and AI can leverage their in-house expertise to build generative AI. This approach not only utilizes the existing skill set of the team but also fosters innovation and growth within. By building in-house, companies can push the boundaries of what's possible with AI, exploring new applications and integrations that might not be available in commercial products.
Long-Term Investment in Innovation
Choosing to build generative AI is a long-term investment in your organization's future. It involves setting up the necessary infrastructure, developing proprietary algorithms, and training models with your data. This investment goes beyond the immediate benefits of the AI application; it builds a foundation for ongoing innovation and adaptation in the rapidly evolving field of AI.
Control Over Data and Compliance
Building your own generative AI solution offers complete control over data usage and compliance. This is particularly crucial for organizations handling sensitive information or operating in heavily regulated industries. By building in-house, companies can ensure that their AI systems comply with all relevant laws and ethical guidelines, reducing the risk of data breaches or compliance issues.
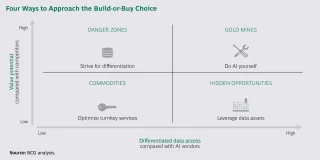
Source: The Build-or-Buy Dilemma in Artificial Intelligence | BCG
Building as a Learning Opportunity
Embarking on a journey to build generative AI is also a significant learning opportunity. It allows teams to gain deep insights into AI technologies and their practical applications. This knowledge is invaluable, not just for the current project but for future technological endeavors and strategic decision-making.
The Building Buzz: Maintaining Competitive Differentiation
In the dynamic landscape of "Build vs. Buy Generative AI," the buzz around building your own generative AI system centers on maintaining competitive differentiation. This approach is not just about having an AI tool; it's about creating a unique asset that sets your organization apart in the market.
Harnessing Unique Capabilities
Building your own generative AI system means you can develop capabilities that are not available in off-the-shelf products. This could involve creating advanced algorithms, integrating AI with proprietary data, or developing solutions for niche problems specific to your industry. Such unique capabilities can become a key differentiator, giving your organization an edge over competitors who rely on standard, widely available AI solutions.
Aligning with Core Business Strategies
For many organizations, especially those with a strong focus on technology, building generative AI aligns closely with their core business strategies. It allows them to not only address current needs but also anticipate future market trends and customer demands. By building in-house, companies can ensure that their AI strategies are in perfect harmony with their long-term business goals, driving innovation and growth.
Creating Intellectual Property
Building your own generative AI contributes to the creation of intellectual property (IP). This IP can be a valuable asset, offering long-term benefits such as licensing opportunities or creating barriers for competitors. Owning the IP for a unique AI solution can also enhance the company's valuation, making it more attractive to investors and stakeholders.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
An in-house generative AI system allows for continuous improvement and adaptation. As the market evolves and new challenges arise, organizations can quickly modify and upgrade their AI systems without being dependent on external vendors. This agility ensures that the AI system remains relevant and effective over time, providing a sustained competitive advantage.
Building as a Brand Statement
Choosing to build generative AI can be a strong brand statement. It showcases the organization's commitment to innovation and technological leadership. This can enhance the brand's reputation in the market, attracting top talent, partners, and customers who are drawn to innovative and forward-thinking companies.
Why Consider Building: Technical and Competitive Advantages
In the realm of "Build vs. Buy Generative AI," the decision to build your own generative AI system is driven by the pursuit of technical and competitive advantages. This approach is not just about leveraging current technology but about shaping the future of your organization's technological landscape.
Tailoring to Specific Technical Requirements
Building your own generative AI allows for the development of solutions that are precisely tailored to meet specific technical requirements. This customization can range from integrating with unique internal systems to addressing niche problems that off-the-shelf solutions cannot solve. By building in-house, organizations can ensure that every aspect of the AI system, from the algorithms to the user interface, is optimized for their specific use case.
Gaining a Competitive Edge
One of the most compelling reasons to build generative AI is the competitive edge it can provide. A custom-built AI system can offer unique functionalities that are not available in the market, setting your organization apart from competitors. This exclusivity in capabilities can be a significant differentiator, especially in industries where technological innovation is a key driver of success.
Leveraging Cutting-Edge Technologies
Building your own system allows you to leverage the latest and most advanced technologies in AI. Organizations that choose to build are often able to experiment with cutting-edge techniques and models, staying ahead of the curve in AI developments. This forward-thinking approach can lead to breakthroughs that can redefine industry standards.
Intellectual Property Creation
Developing your own generative AI system contributes to the creation of valuable intellectual property (IP). This IP can become a strategic asset, offering long-term benefits such as proprietary technology that can be licensed or used to create barriers to entry for competitors. Owning unique AI solutions enhances the company's market position and can be a key factor in attracting investments and partnerships.
Continuous Innovation and Adaptation
An in-house AI system allows for continuous innovation and adaptation to changing market needs and technological advancements. Unlike purchased solutions, which may become outdated or less effective over time, a self-built system can be continually updated and improved, ensuring that it remains at the forefront of AI capabilities.
Advantages of Buying Generative AI
In the "Build vs. Buy Generative AI" debate, opting to buy generative AI solutions offers distinct advantages, particularly for organizations looking to quickly harness the power of AI without the complexities of building from scratch.
Buy In or Lose Out: The Simplicity and Speed of Buying
Buying generative AI solutions stands out for its simplicity and speed. This approach is akin to acquiring a ready-to-use tool, bypassing the lengthy and complex process of development. For organizations without extensive AI expertise or those needing to implement AI solutions rapidly, buying offers a quick entry point into the AI landscape. It eliminates the need for specialized talent recruitment and the intricacies of AI development, allowing companies to focus on applying AI to enhance their operations promptly.
The Buying Bounty: Achieving Parity Quickly
Purchasing off-the-shelf generative AI solutions can quickly bring an organization up to parity with market standards. These solutions, often developed by leading AI vendors, incorporate a wealth of expertise and advanced technology. By buying, companies can immediately benefit from high-quality AI capabilities, which might take years to develop in-house. This approach is particularly beneficial for businesses that need to stay competitive in fast-moving markets where AI is rapidly becoming a baseline expectation.
The Case for Buying: Ease of Implementation and Support
One of the key advantages of buying generative AI is the ease of implementation and ongoing support. Off-the-shelf solutions typically come with vendor support, including training, maintenance, and updates. This reduces the burden on internal IT teams and ensures that the AI systems remain effective and up-to-date with the latest advancements. Additionally, these solutions often integrate seamlessly with existing systems and workflows, making the adoption process smoother and less disruptive to ongoing operations.
Cost and Resource Considerations in Generative AI
When delving into the "Build vs. Buy Generative AI" decision, understanding the cost and resource implications is crucial. This decision impacts not just the financial aspects but also the human resources and long-term investment strategies of an organization.
The Cost Conundrum: Evaluating Financial Implications
The financial implications of building versus buying generative AI are significant and multifaceted. Building in-house involves upfront costs such as hiring expert staff, investing in research and development, and procuring necessary technology and infrastructure. These costs can be substantial but are justified if the solution offers a competitive advantage or is core to the business's operations.
The Talent Tango: Human Resource Considerations
Human resources are another critical factor in the build vs. buy decision. Building generative AI in-house requires a team of skilled professionals, including AI engineers, data scientists, and domain experts. Recruiting and retaining such talent can be challenging and expensive, but it's essential for organizations aiming to develop bespoke AI solutions that offer unique value.
How to Think About the Total Cost of Ownership: Technical, Resource, and Time Requirements
In the "Build vs. Buy Generative AI" decision-making process, understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) is crucial. This includes not just the immediate financial outlay but also the broader implications in terms of technical, resource, and time requirements.
Technical Requirements and Costs
When building generative AI, the technical requirements are extensive. It involves selecting the right algorithms, setting up the necessary infrastructure, and ensuring that the system integrates well with existing technologies. This can be a significant investment, as it requires advanced hardware and software, along with the expertise to develop and maintain these systems. The cost here is not just monetary but also involves the complexity and scalability of the technology being developed.
On the other hand, buying a generative AI solution often means these technical requirements are managed by the vendor. This can reduce the immediate technical burden and associated costs. However, there may be hidden costs in terms of customization and integration with existing systems, which can add up over time.
Resource Allocation and Expenses
Building generative AI in-house requires a dedicated team of experts in AI, machine learning, data science, and related fields. Recruiting and retaining such talent can be costly, and there's also the ongoing expense of training and development. These human resource costs are a significant part of the TCO when building AI solutions.
In contrast, buying generative AI solutions typically requires fewer specialized internal resources. The focus shifts to managing vendor relationships and integrating the AI solution into existing workflows. While this can reduce the direct costs associated with a skilled workforce, it may lead to dependency on external vendors for updates, support, and customization.
Time Investment and Opportunity Costs
Time is a critical factor in the TCO calculation. Building a generative AI solution in-house is a time-intensive process. It involves not just the development phase but also ongoing maintenance and updates. This long-term time commitment can be a significant opportunity cost, as it diverts resources from other potential projects or areas of innovation.
Buying a solution, conversely, can be quicker to deploy. It allows organizations to benefit from AI capabilities almost immediately, without the long development times associated with building in-house. However, there may be time costs in terms of training staff to use the new system and integrating it into existing processes.
Challenges and Strategies in Generative AI Implementation
When navigating the "Build vs. Buy Generative AI" decision, organizations face several challenges in implementing generative AI. These challenges require strategic planning and careful consideration to ensure successful deployment and utilization of AI technologies.
Customization, Compliance, and Time Crunch Challenges
Customization is a major challenge, especially for businesses opting to buy generative AI solutions. Off-the-shelf products may not perfectly align with specific business needs, necessitating additional customization, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Compliance is another critical area, particularly for industries regulated by strict data protection and privacy laws. Building generative AI in-house allows for embedding compliance measures from the start, but it requires a deep understanding of legal requirements. Buying solutions may simplify compliance, but it's essential to ensure that the vendor's solutions meet all necessary regulations.
Support Struggles and Mitigating Investment Risks
Support and maintenance are ongoing challenges, especially for in-house built solutions. Organizations need to ensure they have the necessary expertise and resources for continuous support, updates, and troubleshooting. When buying AI solutions, it's crucial to evaluate the level of support and maintenance offered by the vendor to mitigate these challenges.
Mitigating investment risks involves careful evaluation of both the immediate and long-term costs and benefits of the AI solution. Organizations must consider not only the financial investment but also the potential impact on business operations and the ability to adapt to future technological advancements.
Use and Protect Data: Ensuring Data Security and Integrity
Data security and integrity are paramount in generative AI implementation. For in-house solutions, organizations must establish robust data governance frameworks to protect sensitive information and ensure data integrity. When buying AI solutions, it's crucial to assess the vendor's data security measures and policies to ensure they align with the organization's data protection standards.
The Role of Partnerships in Generative AI
In the context of "Build vs. Buy Generative AI," partnerships play a pivotal role in successfully implementing and scaling generative AI capabilities. Collaborating with external entities can provide a balanced approach, combining the strengths of building in-house with the advantages of buying from external vendors.
A Partner Strategy: Scaling Rapidly and Effectively
Adopting a partner strategy in generative AI allows organizations to scale their AI capabilities more rapidly and effectively. This approach involves collaborating with companies that have complementary strengths or resources. For instance, a business with a robust customer base might partner with a firm that has advanced AI technology but lacks market access. Such partnerships can accelerate the deployment of AI solutions and enhance their effectiveness.
Collaborative Approaches: Leveraging External Expertise
Collaborative approaches in generative AI involve leveraging the expertise and resources of external partners. This can include joint development projects, where both parties contribute their unique skills and knowledge to create a more robust AI solution. For example, a business might partner with an AI research firm to develop a custom solution that combines the business's domain expertise with the research firm's technical knowledge.
Making an Informed Decision in Generative AI
In the dynamic landscape of "Build vs. Buy Generative AI," making an informed decision is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage the power of AI effectively. This decision is not just about choosing between two options but understanding the nuances and implications of each path.
Major Investments and Strategic Differentiation
When considering building generative AI, organizations must recognize the major investments required. This includes not only financial resources but also time and human capital. Building in-house allows for strategic differentiation, as it enables the creation of unique, tailored AI solutions that can provide a competitive edge. However, this route demands a significant commitment to developing, maintaining, and updating the AI system, which can be a challenging endeavor for many organizations.
Decision Dilemma: Balancing Innovation with Risk Management
The decision dilemma in generative AI revolves around balancing the desire for innovation with the need for risk management. Building in-house offers the potential for groundbreaking innovation and customization but comes with higher risks, including the potential for higher costs and resource allocation challenges. On the other hand, buying AI solutions can mitigate some of these risks by providing tested and supported solutions, but it may limit the organization's ability to innovate and differentiate in the market.
The Answer Isn’t “Do Nothing”: Proactive Decision-Making
In the face of this complex decision-making landscape, the answer isn’t to “do nothing.” Proactive decision-making is essential. Organizations must assess their capabilities, resources, and long-term strategic goals to determine which approach aligns best with their objectives. This may involve a thorough analysis of the market, understanding the potential ROI of different AI solutions, and considering how these solutions fit into the broader business strategy.
Conclusion
The decision to build, buy, or partner in the realm of generative AI depends on an organization's specific needs, capabilities, and strategic goals. It requires a careful assessment of the potential return on investment, the ability to manage risks, and the long-term impact on the organization's market position. By considering these factors, organizations can make an informed decision that aligns with their objectives and positions them for success in the evolving landscape of AI technology.