Can We Balance AI and Data Privacy? The Challenge in 2024
Written By
Published On
Read Time

As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more integrated into our daily lives, it's crucial for both businesses and individuals to grasp how AI interacts with data privacy. AI is reshaping business operations by automating tasks and offering insights based on data. This article will explore how AI and data privacy intersect, highlighting potential risks, legal obligations, and ways organizations can comply with privacy laws. We'll also share resources to help navigate the complex relationship between AI and data privacy.
Data privacy is about individuals' rights to control their personal information and its usage. It's vital for organizations to consider this as they implement and use artificial intelligence.
Ethical AI and Data Privacy: Navigating Challenges and Best Practices
In the age of rapid technological advancement, the intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and data privacy has become a critical area of focus. As AI technologies evolve, they bring about significant benefits but also pose unique challenges to data privacy. This content combines insights from various sources to provide a comprehensive overview of ethical AI and data privacy, highlighting the challenges and best practices for navigating this complex landscape.
Best Practices for Ethical AI and Data Privacy
Establish Governance Models: Organizations should set up governance models to monitor AI and data privacy requirements, ensuring compliance across all operations.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Legal requirements evolve rapidly, necessitating continuous monitoring and the agility to adapt to new regulations.
Invest in Training: Providing training on emerging technologies and legal requirements is crucial for professionals to navigate the AI landscape responsibly.
Promote Transparency and Accountability: AI systems should be designed to be transparent in their operations and accountable for the data they process.
Encourage Ethical AI Use: Encouraging the ethical use of AI by emphasizing its role as a tool to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them is essential for fostering innovation while protecting user privacy.
The Artificial Intelligence Landscape Today
The artificial intelligence (AI) landscape today is a complex and rapidly evolving field, deeply intertwined with the issue of data privacy. As AI technologies become more sophisticated and integrated into various sectors, the balance between innovation and privacy protection has emerged as a critical concern. This landscape is shaped by advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, deep learning, and generative AI, each bringing unique capabilities and challenges to the forefront of technology and society.
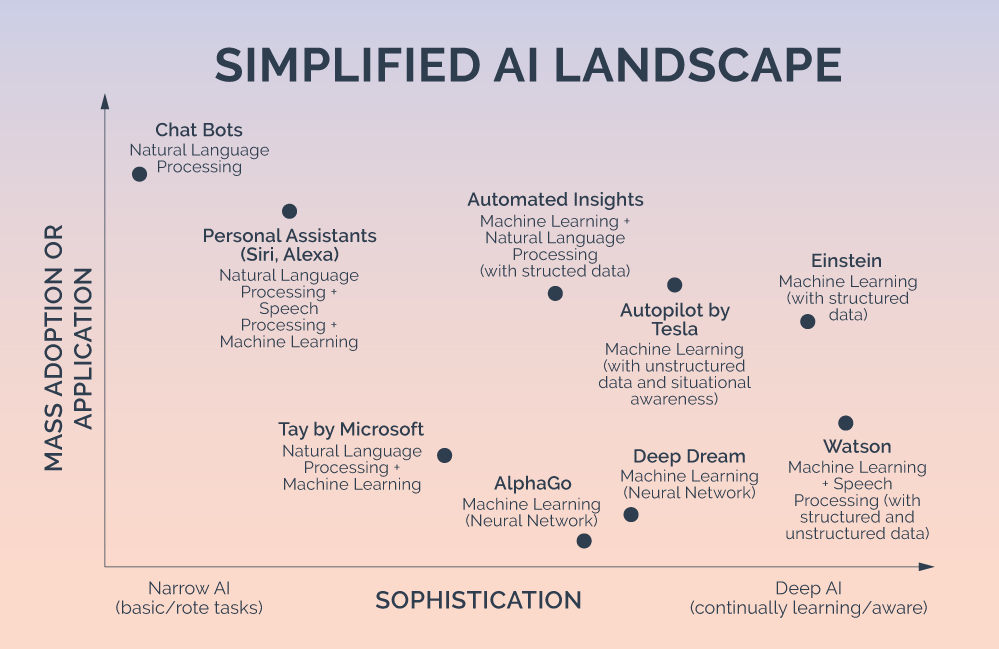
Advancements and Integration
AI's growth is fueled by significant advancements in computational power, data availability, and algorithmic efficiency. From voice assistants and chatbots to predictive analytics and autonomous systems, AI's applications are vast and varied. These technologies rely heavily on large datasets to learn and make decisions, raising important questions about the use and protection of personal data. The integration of AI into everyday life has made it a pivotal element in shaping future societies, economies, and governance models.
Data Privacy Concerns
As AI systems process vast amounts of data, including sensitive personal information, concerns over data privacy have become more pronounced. The ability of AI to analyze and predict behavior patterns has led to fears over surveillance, bias, and loss of anonymity. The use of AI in decision-making processes, without transparent mechanisms, further complicates the landscape, making it difficult for individuals to understand how their data is being used and for what purposes.
Ethical and Responsible AI
The call for ethical and responsible AI is gaining momentum among developers, corporations, and policymakers. This involves the development of AI systems that are not only efficient and effective but also fair, transparent, and accountable. Ethical AI practices include ensuring data privacy, mitigating biases, and enabling users to have control over their personal information. Companies and organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of these practices in maintaining public trust and compliance with legal standards.
The Future Landscape
Looking ahead, the AI landscape is set to continue its rapid expansion, with emerging technologies like generative AI and federated learning offering new possibilities for innovation while potentially addressing some privacy concerns. Federated learning, for example, allows for the collaborative training of AI models without sharing the underlying data, offering a promising approach to privacy-preserving AI development.
What Are the Current Efforts to Regulate AI?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), the question of how to effectively regulate this technology while ensuring the protection of data privacy is paramount. Governments, regulatory bodies, and industry leaders worldwide are engaged in a complex dialogue to establish frameworks and guidelines that balance innovation with ethical considerations and privacy safeguards. This section explores the current efforts to regulate AI, highlighting key initiatives and their implications for AI and data privacy.
The European Union's AI Act
The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of regulatory efforts with its proposed AI Act, setting a precedent for comprehensive AI regulation on a global scale. The AI Act is designed to provide a harmonized regulatory framework for AI within the EU, categorizing AI systems based on their risk levels and applying corresponding requirements. This act focuses on high-risk AI applications, demanding transparency, accuracy, and security to protect individuals' rights and privacy. The AI Act reflects the EU's commitment to ensuring that AI technologies are developed and used in a way that respects fundamental rights and values, including privacy and data protection.

GDPR and AI
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is another cornerstone of the EU's approach to regulating AI, emphasizing the protection of personal data. Although not specifically designed for AI, GDPR's principles of data minimization, purpose limitation, and consent are highly relevant to AI applications. GDPR requires that any processing of personal data by AI systems must be lawful, fair, and transparent, providing individuals with control over their data. This regulation has prompted organizations to reassess their AI strategies, ensuring compliance and enhancing data privacy measures.
Global and Regional Initiatives
Beyond the EU, other regions and countries are developing their regulatory approaches to AI. For example, the United States has introduced the AI Bill of Rights as a non-binding framework to guide the ethical development and deployment of AI technologies, emphasizing privacy, transparency, and accountability. Similarly, China has issued guidelines and ethical norms for AI, focusing on promoting responsible AI development that respects privacy and public interests.
Industry Standards and Ethical Guidelines
In addition to governmental regulations, industry groups and organizations are actively working to establish standards and ethical guidelines for AI. These efforts include the development of best practices for data privacy, security measures, and ethical considerations in AI applications. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) are among those leading the charge in creating voluntary standards that guide the responsible use of AI technologies.
Challenges and Future Directions
While these regulatory efforts represent significant steps toward ensuring the ethical use of AI, challenges remain. The rapid pace of AI development, coupled with the technology's global reach, complicates the creation of a unified regulatory framework. Moreover, balancing innovation with regulation requires ongoing dialogue among stakeholders, including policymakers, technologists, businesses, and civil society.
Ethical and Responsible Use of AI: What Can Organizations Do Today?
In the context of growing concerns around AI and data privacy, organizations are increasingly called upon to adopt ethical and responsible practices in their AI deployments. The balance between leveraging AI for its immense potential benefits and ensuring the protection of individual privacy rights is delicate and requires a proactive approach. Here’s what organizations can do today to foster an environment where AI contributes positively to society while safeguarding data privacy.
Establish Clear Governance Structures
One of the first steps organizations can take is to establish clear governance structures for AI and data privacy. This involves setting up dedicated teams or committees that focus on ethical AI use, data protection, and compliance with relevant regulations. These governance bodies should have a clear mandate to oversee AI projects, ensuring they align with ethical standards and legal requirements. By doing so, organizations can ensure that AI applications are developed and deployed in a manner that respects privacy and promotes trust.
Implement Privacy by Design
Adopting a privacy by design approach is crucial for organizations looking to use AI responsibly. This means integrating data privacy considerations into the development phase of AI systems, rather than addressing them as an afterthought. Privacy by design involves minimizing data collection to what is strictly necessary, securing data through encryption and other measures, and providing users with control over their personal information. By embedding these principles into AI systems from the outset, organizations can significantly reduce privacy risks.
Foster Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are key pillars of ethical AI use. Organizations should be open about how their AI systems operate, the data they collect, and the purposes for which it is used. This includes providing clear and accessible privacy policies, as well as mechanisms for users to inquire about and manage their data. Additionally, organizations should implement robust auditing and reporting processes to monitor AI systems' performance and impact, ensuring they function as intended and do not infringe on privacy rights.
Engage in Continuous Learning and Improvement
The AI landscape is continuously evolving, with new technologies, challenges, and regulatory developments emerging regularly. Organizations must commit to ongoing learning and improvement to stay ahead of these changes. This can involve investing in training for staff, staying abreast of the latest research and best practices in ethical AI, and engaging with external experts and stakeholders. Continuous learning enables organizations to refine their AI applications over time, addressing emerging privacy concerns and adapting to new regulatory requirements.
Collaborate on Ethical AI Initiatives
Collaboration is essential for advancing ethical AI practices. Organizations can benefit from joining industry groups, participating in forums, and engaging in partnerships focused on responsible AI use. These collaborative efforts can facilitate the sharing of knowledge, experiences, and best practices, helping to raise standards across the board. Additionally, collaboration with regulatory bodies, civil society, and academia can help organizations navigate the complex ethical and regulatory landscape surrounding AI and data privacy.
Three Ways to Stay on Top of Evolving AI and Data Privacy Rules
Navigating the complex landscape of AI and data privacy requires organizations to be proactive, informed, and adaptable. As regulations evolve and the capabilities of AI expand, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting user privacy. Here are three strategies organizations can employ to effectively manage the challenges posed by the dynamic nature of AI and data privacy rules.
Establish Data Privacy and AI Governance Teams
Creating dedicated governance teams is a foundational step for organizations aiming to responsibly manage AI and data privacy. These teams should comprise experts from various disciplines, including legal, technical, and ethical backgrounds, to provide a holistic approach to AI governance. Their responsibilities include:
Developing and Implementing Policies: Crafting clear, comprehensive policies that address data privacy in the context of AI usage is critical. These policies should reflect current regulations, ethical considerations, and best practices in AI development and deployment.
Oversight and Compliance: Governance teams should oversee AI projects to ensure they comply with both internal policies and external regulations. This includes regular audits and assessments to identify and mitigate potential privacy risks.
Cross-functional Coordination: These teams act as a bridge between different departments, ensuring that AI initiatives across the organization align with privacy and ethical standards. By fostering communication and collaboration, governance teams can ensure a unified approach to AI and data privacy.
Monitor Continuously and Agilely
The regulatory landscape for AI and data privacy is continuously changing, with new laws, guidelines, and standards emerging regularly. Organizations must adopt a flexible and vigilant monitoring approach to stay compliant and protect user privacy effectively.
Stay Informed: Keeping abreast of regulatory changes and industry trends is essential. This can involve subscribing to legal and industry newsletters, participating in relevant forums, and engaging with regulatory bodies.
Adaptive Frameworks: Develop frameworks that allow for quick adaptation to new regulations. This includes having scalable and flexible AI systems that can be easily adjusted to meet changing privacy requirements.
Engage with Stakeholders: Regularly engaging with stakeholders, including users, employees, and regulators, can provide valuable insights into potential privacy concerns and emerging regulatory expectations. This engagement can also help in anticipating future changes and preparing accordingly.
Invest in Training
Investing in comprehensive training programs is crucial for ensuring that all members of an organization understand the importance of AI and data privacy, as well as their roles in maintaining it.
Regular Training Sessions: Conduct regular training sessions for employees across all levels of the organization. These sessions should cover the latest developments in AI and data privacy laws, organizational policies, and ethical considerations.
Specialized Training for AI Teams: Teams directly involved in AI development and deployment should receive specialized training that covers technical aspects of data privacy, including data anonymization techniques, secure data storage and transmission, and privacy-preserving AI models.
Promote a Culture of Privacy: Beyond formal training, organizations should strive to cultivate a culture that values and prioritizes privacy. This can involve internal campaigns, sharing best practices, and recognizing individuals or teams that contribute to enhancing privacy protections.
Expert Insights on AI and Privacy
In the rapidly evolving domain of artificial intelligence (AI), the conversation around data privacy is becoming increasingly nuanced and critical. Experts like Lucille Bonenfant and Diane Gutiw are at the forefront of shaping how organizations approach the balance between leveraging AI for innovation and ensuring stringent data privacy protections. Their insights provide valuable guidance for navigating the complex interplay between AI advancements and privacy concerns.
Lucille Bonenfant: Vice-President and Chief Privacy Officer
Lucille Bonenfant, serving as Vice-President and Chief Privacy Officer, emphasizes the importance of establishing robust data protection strategies in the age of AI. Bonenfant advocates for a proactive approach to privacy, where organizations not only comply with existing regulations like GDPR but also anticipate future privacy challenges that AI technologies may pose. She highlights the necessity of integrating privacy considerations into the AI development process from the outset, a practice known as "privacy by design."
Bonenfant's perspective underscores the critical role of governance in managing AI and data privacy. She suggests that organizations should set up dedicated governance teams responsible for overseeing AI projects, ensuring they adhere to ethical standards, legal requirements, and best practices in data protection. These teams play a crucial role in developing and implementing privacy policies, conducting regular audits, and fostering a culture of privacy across the organization.
Diane Gutiw: Vice-President and Global AI Research Lead
Diane Gutiw, the Vice-President and Global AI Research Lead, focuses on the intersection of AI research and ethical considerations. Gutiw's work involves exploring the potential of AI technologies while addressing the inherent risks related to data privacy and security. She emphasizes the importance of responsible AI use, advocating for transparency, accountability, and user control over personal data.
Gutiw points out the challenges of ensuring AI systems are transparent and understandable to users, especially when it comes to how their data is being used and for what purposes. She advocates for the development of AI systems that are not only efficient and effective but also fair and equitable. This includes addressing biases in AI algorithms and ensuring that AI applications do not inadvertently compromise user privacy.
Uncovering the Hidden Risks of AI
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into various sectors has been transformative, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency. However, this rapid advancement brings with it a suite of hidden risks, particularly concerning data privacy and security. Understanding these risks is crucial for organizations, developers, and regulatory bodies to mitigate potential threats effectively.
Security Concerns with Language Models and Generative AI Platforms
Language models and generative AI platforms, such as those used in natural language processing and content creation, pose unique security concerns. These systems process vast amounts of data, including sensitive personal information, to learn and generate outputs. This raises significant questions about access control, data storage, and transmission security.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for these AI models to inadvertently leak personal data or be manipulated to generate misleading information. For instance, if a language model is trained on datasets containing private information without proper anonymization, it could potentially reproduce this information in its outputs, leading to privacy breaches.
Moreover, generative AI platforms can be used to create deep fakes or synthetic media that are indistinguishable from real content. This capability poses risks not only to individual privacy but also to the integrity of information, as it can be exploited to spread misinformation or conduct phishing attacks.
Regulatory Bodies and Their Role in AI Security
Regulatory bodies play a pivotal role in ensuring AI security and protecting data privacy. By establishing comprehensive guidelines and standards, they provide a framework within which AI technologies can be developed and deployed safely.
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets a precedent for how personal data should be handled, including data processed by AI systems. The GDPR emphasizes principles such as data minimization, purpose limitation, and user consent, which are crucial for maintaining privacy in AI applications.
Similarly, initiatives like the proposed EU AI Act aim to categorize AI systems based on their risk levels and apply corresponding regulatory requirements. High-risk applications, which have significant implications for individual rights and safety, are subject to stricter scrutiny and compliance obligations.
Security Considerations for Businesses Using AI Products
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), businesses leveraging AI products face a unique set of security considerations. Ensuring the protection of data privacy is paramount, as AI systems often process vast amounts of sensitive information. Here are key security considerations businesses should keep in mind:
Implement Robust Data Protection Measures
Businesses must prioritize the implementation of robust data protection measures. This includes encrypting data both in transit and at rest, employing strong access controls, and regularly updating security protocols to guard against new vulnerabilities. AI systems should be designed with privacy in mind, incorporating principles like data minimization and purpose limitation to ensure that only necessary data is collected and used for clearly defined purposes.
Choose AI Partners Wisely
Selecting AI partners and vendors with a strong security track record is crucial. Businesses should conduct thorough due diligence, assessing potential partners' data privacy and security practices. This includes evaluating their compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR and their commitment to ethical AI development. Partnering with reputable AI providers can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes
The regulatory landscape for AI and data privacy is constantly changing. Businesses must stay informed about new laws and guidelines that could affect their AI applications. This involves not only monitoring developments in jurisdictions where the business operates but also understanding global trends that could influence future regulations. Compliance with current regulations and proactive adaptation to emerging laws are essential for mitigating legal and reputational risks.
Foster a Culture of Privacy and Security
Creating a culture that values privacy and security across the organization is vital. This includes training employees on the importance of data protection, the ethical use of AI, and the potential risks associated with AI technologies. Encouraging open dialogue about privacy and security concerns can help identify potential issues early and foster a proactive approach to risk management.
Security Considerations for General Users of AI
For general users interacting with AI systems, whether through consumer applications, online services, or smart devices, understanding the security implications is key to protecting personal data. Here are essential security considerations for users:
Be Cautious with Personal Data
Users should exercise caution when sharing personal information with AI systems. This includes being mindful of the data provided to virtual assistants, chatbots, and other AI-powered services. Users should review privacy settings and opt for configurations that offer maximum data protection, limiting the amount of personal information shared.
Understand Data Usage Policies
Before using AI-powered services, users should familiarize themselves with the providers' data usage policies. Understanding how their data will be used, stored, and shared can help users make informed decisions about their engagement with AI technologies. Look for services that are transparent about their data practices and offer users control over their information.
Use Secure Connections
When interacting with AI applications, ensuring a secure connection can protect against data interception and unauthorized access. This includes using encrypted connections (HTTPS) and being wary of public Wi-Fi networks when accessing AI services. Additionally, users should keep their devices and software updated to protect against security vulnerabilities.

Stay Informed About AI Developments
General users can benefit from staying informed about developments in AI and data privacy. Awareness of potential risks and the latest best practices for data protection can empower users to navigate the AI landscape more safely. This includes understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI technologies and being skeptical of AI-generated content that seems suspicious or too good to be true.
Don't Blindly Trust AI
In the world of artificial intelligence (AI), the marvels of technology often come with a caveat: the importance of not blindly trusting AI systems. As AI continues to permeate various aspects of our lives, from personal assistants to complex decision-making tools, the need for a critical perspective on its outputs becomes increasingly paramount. This skepticism is particularly crucial when it comes to issues of AI and data privacy, where the stakes involve the protection of personal and sensitive information.
AI systems, including language models and generative AI platforms, are designed to process and generate information based on vast datasets. While these technologies can offer highly accurate and insightful outputs, they are not infallible. The data used to train AI models may contain biases, inaccuracies, or outdated information, which can lead to flawed conclusions or recommendations. Moreover, the algorithms themselves might not fully grasp the nuances of human contexts, leading to potential privacy breaches or misuse of data.
AI as an Assistant, Not a Replacement
The narrative surrounding AI often oscillates between utopian visions of technological omnipotence and dystopian fears of human obsolescence. However, a more balanced and productive view is to consider AI as an assistant rather than a replacement for human capabilities. This perspective is especially relevant in discussions about AI and data privacy, where the complementary strengths of humans and machines can be harnessed to safeguard personal information while driving innovation.
AI's capacity to process and analyze data at scale can provide invaluable support in identifying privacy risks, automating data protection measures, and enhancing security protocols. However, the oversight, ethical judgment, and contextual understanding required to navigate privacy concerns necessitate human involvement. Humans bring to the table critical thinking, ethical considerations, and creative problem-solving skills that AI currently cannot replicate.
AI Limitations and the Myth of World Domination
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has sparked a wide range of discussions and debates, not least among them the concern over AI's potential to achieve world domination. This notion, often fueled by sensationalized media portrayals and speculative fiction, overlooks the inherent limitations of AI technologies and the rigorous efforts in place to ensure ethical use and data privacy. Understanding these limitations is crucial in demystifying AI and fostering a realistic perspective on its role in society.
Understanding AI's Technical Limitations
At its core, AI is a tool created by humans to process data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on the information it has been trained on. Despite its impressive capabilities, AI lacks consciousness, emotional understanding, and the ability to comprehend complex moral and ethical considerations. Its functionality is confined to the scope defined by its creators, meaning AI operates within a set of limitations determined by current technology, data availability, and programming constraints.
For instance, AI's decision-making process is heavily reliant on the quality and breadth of the data it is trained on. Biases in the data can lead to skewed outcomes, underscoring the importance of diverse, accurate, and comprehensive datasets. Furthermore, AI systems often lack the ability to explain their reasoning in understandable terms, a limitation known as the "black box" problem, which poses significant challenges for transparency and accountability.
Ethical Safeguards and Data Privacy
The global AI community, including researchers, developers, and policymakers, is acutely aware of these limitations and the potential risks associated with AI technologies. As a result, considerable effort is being directed towards establishing ethical guidelines, regulatory frameworks, and privacy protections to govern AI development and application. Initiatives like the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and proposed AI Act are examples of how regulatory bodies are working to ensure AI technologies respect user privacy and ethical standards.
Organizations and developers are encouraged to adopt principles of ethical AI use, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and fairness. This includes conducting impact assessments, implementing privacy-by-design approaches, and ensuring users have control over their personal data. By addressing AI's limitations and potential risks head-on, the AI community aims to mitigate concerns over privacy breaches and unethical use.
Dispelling the Myth of World Domination
The myth of AI achieving world domination stems from a misunderstanding of AI's capabilities and an underestimation of the comprehensive measures in place to ensure its ethical use. AI, with its current limitations, is far from possessing the autonomy or intentionality required to dominate the world. Instead, it remains a powerful tool that, when used responsibly and ethically, has the potential to drive significant advancements across various sectors.
Final Thoughts
The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and data privacy is a dynamic and complex field, marked by rapid advancements in technology and evolving regulatory landscapes. As AI continues to integrate into every facet of our lives, from personal assistants to predictive analytics in healthcare and finance, the imperative to balance innovation with the protection of individual privacy has never been more critical. The insights gathered from the discussions in the aforementioned blogs underscore the multifaceted challenges and opportunities that lie at the heart of AI and data privacy.
AI's potential to transform industries, streamline processes, and unlock new avenues of innovation is immense. However, this potential comes with significant responsibilities, particularly regarding the ethical use of AI and the safeguarding of personal data. The discussions highlight the importance of adopting a proactive approach to privacy, one that anticipates potential risks and embeds privacy considerations into the development and deployment of AI technologies from the outset.